Human Excretory System
Human Excretory System: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Vasa recta, Juxtaglomerular Apparatus, Distal Convoluted Tubule & Collecting Ducts etc.
Important Questions on Human Excretory System
Glomeruli are confined to
Formation of concentrated (hyperosmotic) urine in vertebrates generally depends on
What drains the major Calyx?
The major calyx surrounds the apex of the malpighian pyramids.
The walls of renal pelvis consists of a mucosal lining of _____ epithelium.
State the function of major and minor calyses.
Explain how major calyx is formed?
Mention the site where the minor calyx is formed?
Minor calyx surrounds renal _____ (papillae/tubule) of each pyramid.
Write one difference between major and minor calyx.
Minor calyx is found to be present in the liver.
Which of the following is NOT lined by squamous epithelium?
The medulla is compossed of a finely striped substance arranged in several conical _____.
Seven million nephrons are present in two kidneys.
Name the structural and functional unit of the kidney. (Scientific term)
Reabsorption of the useful products takes place in the distal convoluted tubule part of the renal tubule in the human body.
Select the correct statement
The given diagram represents a single nephron from a mammalian kidney. Identify which of the numbered regions is
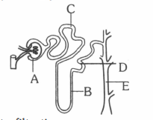
I. The site of ultrafiltration
II. Particularly sensitive to ADH
III. The main site for the reaborption of glucose and amino acid
IV. Largely responsible for the adjustment of blood pH
Match the excretory functions of section I with the parts of the excretory system in section II. Choose the correct combinations from among the answers given
| Section I | Section II | ||
| (i) | Ultrafiltration | (a) | Henle's loop |
| (ii) | Concentration of urine | (b) | Ureter |
| (iii) | Transport of urine | (c) | Urinary bladder |
| (iv) | Storage of urine | (d) | Malpighian corpuscles |
| (e) | Proximal convoluted tubules | ||
A fall in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) activates
